* Represents a beginning to a new page.
Examples are in purple.
Using the Factored Form:
1. You can quickly find the roots by solving the quadratic.
example: 0= x² + 5x + 6
0= (x+2)(x+3)
x= -2 x= -3
Roots at x= -2, x= -3
2. You can find the x-coordinate of the vertex by finding the midpoint of the roots.
example: Xv= (-2) + (-3) / 2
Xv= -5/2
3. Once you know the x-coordinate of the vertex you can substitute back into the equation to find the y-coordinate of the vertex.
example: F(-5/2) = (-5/2)² + 5(-5/2) + 6
F(-5/2) = -1/4
Therefore the vertex is at (-5/21, -1/4)
The General Form for the Equation of a Parabola:
F(x) = ax² + bx + c
The Role of Parameter b:
b produces an obligue translation.
The Role of Parameter c:
c is the y-intercept of the parabola. It's coordinates are (0,0)
*Completing the Square:
PROCEDURE:
1. Factor the coefficents of x² out of the two
terms. Leave some "space" in the brackets.
y= 3x² + 12x -5
y= 3(x² + 4x )-5
2. Divide the coefficent of the x term by 2 and square the result.
4/2 = 2
2² = 4
3. Add and subtract the result from step2 inside
the brackets [you just "completed the square"]
y= 3(x² + 4x + 4x -4x) -5
4. Factor the first three terms in the brackets into
a perfect square.
y= 3[(x+2)² -4] -5
5. Distribute the number outside the brackets.
y=3(x+2)² -12 -5
6. Simplify
y=3(x+2)² -17
*Sinusoidal Graphs:
F(x) = AsinB(x-C) + D or F(x)= ACos B(x-C) + D
The Basic Function Graphs:
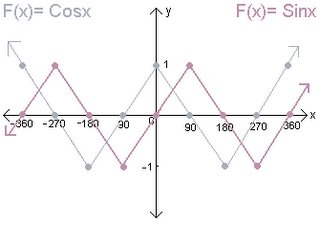
The Role of Parameter A:
/A/ is called the Amplitude or the "vertical strecth." It tells you the distance from the sinusoidal axis to the maximum or minimum value.
The Role of Paramere B:
